Moles (nevi)
What are moles?
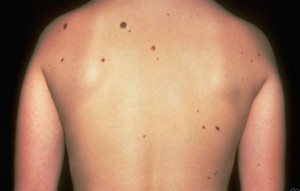 Moles are common normal growths of the skin due to nests of cells called melanocytes. Melanocytes are the cells in our skin responsible for the development of pigmentation. Almost every adult has a few moles and adults with a fair complexion often have more moles. It is normal to have 10 to 40 moles. Individuals with more than 50 moles are at a slightly increased risk of developing an abnormal mole throughout the course of their lifetime.
Moles are common normal growths of the skin due to nests of cells called melanocytes. Melanocytes are the cells in our skin responsible for the development of pigmentation. Almost every adult has a few moles and adults with a fair complexion often have more moles. It is normal to have 10 to 40 moles. Individuals with more than 50 moles are at a slightly increased risk of developing an abnormal mole throughout the course of their lifetime.
Benign moles generally exhibit the following traits:
- 1 color – Often brown, but a mole can be tan, black, red, pink, blue, skin-toned, or colorless
- Round in shape
- Flat or slightly raised
- Appears the same from month to month
Moles often exhibit various sizes and shapes even in the same person. Moles may have hairs within them. This finding is often considered a benign sign. Some moles will change slowly over time, possibly even disappear. Moles may appear anywhere on the skin, even on locations never exposed to the sun. They may develop on the scalp, between the fingers and toes, on the soles and palms, or under the nails.
What is an atypical mole or dysplastic nevus?
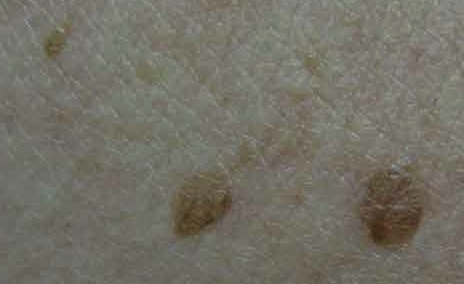 When the dermatologist evaluates your moles on physical examination certain features of the mole may prompt a biopsy. When the pathologist evaluates the moles they are categorized or graded depending on the appearance of the cells underneath the microscope. They may be:
When the dermatologist evaluates your moles on physical examination certain features of the mole may prompt a biopsy. When the pathologist evaluates the moles they are categorized or graded depending on the appearance of the cells underneath the microscope. They may be:
- Benign or normal
- Slightly abnormal or mild dysplasia
- Moderately abnormal or moderate dysplasia
- Severely abnormal or severe dysplasia
- Melanoma
If the mole is read as abnormal, then traditionally another procedure in the office is performed to remove additional skin to ensure all of the abnormal cells are removed. This procedure is referred to as an excision and typically requires stitches.
Congenital mole
When a person is born with a mole, the mole is referred to as a congenital mole. Approximately, 1:100 people is born with a mole. These moles vary in size from small to giant. Having giant congenital moles increases an individual’s risk of developing melanoma.

